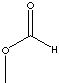
| METHYL
FORMATE
|
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. |
107-31-3 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 203-481-7 | |
| FORMULA | HCOOCH3 | |
| MOL WT. | 60.05 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2915.13 |
|
| TOXICITY | Oral rat LD50: 1500 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Methyl methanoate; Formic acid methyl ester; R 611; | |
|
Formiate de methyle; Formiate De Methyle (French); Methylester Kyseliny Mravenci; Methylformiaat; Methylformiaat (Dutch); Methylformiat Methylformiat (German); Metil (Formiato Di); Metil (Formiato Di) (Italian); Mravencan Methylnaty; |
||
| DESCRIPTION | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
colorless liquid with an ether like odor. |
|
| MELTING POINT |
-100 C |
|
| BOILING POINT | 32 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.98 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
soluble |
|
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
miscible with most organic solvents |
|
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | 2.07 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
449 C |
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 4 ; Reactivity: 1 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.3430 |
|
| FLASH POINT |
-32.5 C |
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Formic acid, also called methanoic acid), is the simplest and has the lowest mole weight of the carboxylic acids, in which a single hydrogen atom is attached to the carboxyl group (HCOOH). If a methyl group is attached to the carboxyl group, the compound is acetic acid. It occurs naturally in the body of ants and in the stingers of bees. Functionally, it is not only an acid but also an aldehyde; it reacts with alcohols to form esters as an acid and it is easily oxidized which imparts some of the character of an aldehyde. Pure formic acid is a colorless, toxic, corrosive and fuming liquid, freezing at 8.4 C and boiling at 100.7 C. It is soluble in water, ether, and alcohol. It irritates the mucous membranes and blisters the skin. It is prepared commercially from sodium formate with the reaction of condensed sulfuric acid. Formic acid is used as a chemical intermediate and solvent, and as a disinfectant. It is also in processing textiles and leathers, electroplating and coagulating latex rubber. Methyl formate, methyl ester of formic acid, is a clear liquid with a pleasant odor; very soluble in water and miscible with most organic solvents. It is readily hydrolyzed by water. Commercial methyl formate is produced from methanol with carbon monoxide in the presence of strong base. The predominant use of methyl formate is in the preparation of formamide and dimethylformamide. They are used as important solvent for PUR coatings, imitation leather and for the production of PAN fibres. They are used as a reaction medium for the pharmaceutical preparation. Methyl formate is used as the raw material of formic acid which find application as a chemical intermediate and solvent, in processing textiles, leathers, electroplating, in coagulating latex rubber, and as a disinfectant. This ester has the properties of high volatility, high vapor pressure, low viscosity and low surface tension. Accordingly, it is commonly used as a component of the solvent system to achieve quick drying coating finishes and in spray applications. It is used as a component of azeotrope to recover expensive solvents. It is also used as a blowing agent for expanded synthetic rubbers. It is used as an intermediate to manufacture various organic chemicals including pharmaceuticals, optical brighteners and hydrocyanic acid. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
colorless liquid with an ether like odor |
|
|
ASSAY |
97.0% min |
|
| WATER |
0.05% max |
|
|
ACIDITY |
0.05% max |
|
|
COLOR |
25 max (Pt/Co scale) |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 200kgs in Drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 3 (Packing group: I) | |
| UN NO. | 1243 | |
| REMARKS | ||
|
methyl formate is a highly flammable liquid and a dangerous fire hazard. |
||